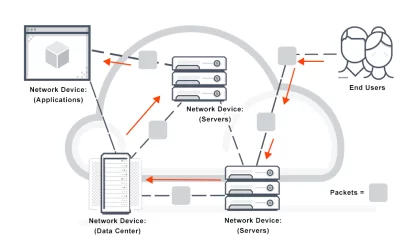
MPLS is a mechanism in high-performance telecommunications networks that directs data from one network node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses, avoiding complex lookups in a routing table. The labels identify virtual links (paths) between distant nodes rather than endpoints. MPLS can encapsulate packets of various network protocols. MPLS supports a range of access technologies, including T1/E1, ATM, Frame Relay, and DSL.
MPLS header consists of following.
· Label (20 bits)
· QoS (3 bits)
· Bottom of Stack (1 bit)
· Time To Live (8 bits)
And a MPLS network consist of two types of routers namely Label Edge Router (LER) and Label Switch Router (LSR).
LSR: Routers that perform routing based on labels.
LER: Routers that are in the entry and exit points of the MPLS network. They push a MPLS label into the packets which are coming into the MPLS network and pop off the MPLS labels from the packets leaving the MPLS network. Refer Figure: MPLS.