A spanning tree is a subset of Graph G, which has all the vertices covered with minimum possible number of edges. Hence, a spanning tree does not have cycles and it cannot be disconnected..
By this definition, we can draw a conclusion that every connected and undirected Graph G has at least one spanning tree. A disconnected graph does not have any spanning tree, as it cannot be spanned to all its vertices.
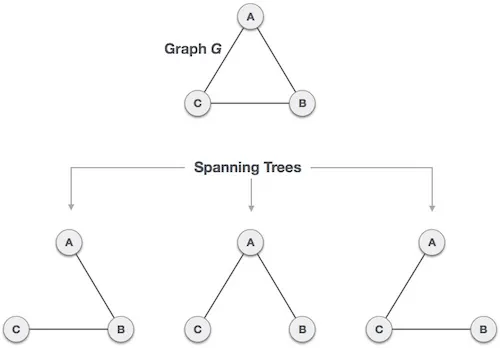
We found three spanning trees off one complete graph. A complete undirected graph can have maximum nn-2 number of spanning trees, where n is the number of nodes. In the above addressed example, n is 3, hence 33−2 = 3 spanning trees are possible.
General Properties of Spanning Tree
We now understand that one graph can have more than one spanning tree. Following are a few properties of the spanning tree connected to graph G −
v A connected graph G can have more than one spanning tree.
v All possible spanning trees of graph G, have the same number of edges and vertices.
v The spanning tree does not have any cycle (loops).
v Removing one edge from the spanning tree will make the graph disconnected, i.e. the spanning tree is minimally connected.
v Adding one edge to the spanning tree will create a circuit or loop, i.e. the spanning tree is maximally acyclic.
Mathematical Properties of Spanning Tree
Ø Spanning tree has n-1 edges, where n is the number of nodes (vertices).
Ø From a complete graph, by removing maximum e – n + 1 edges, we can construct a spanning tree.
Ø A complete graph can have maximum nn-2 number of spanning trees.
Thus, we can conclude that spanning trees are a subset of connected Graph G and disconnected graphs do not have spanning tree.
Application of Spanning Tree
Spanning tree is basically used to find a minimum path to connect all nodes in a graph. Common application of spanning trees are −
· Civil Network Planning
· Computer Network Routing Protocol
· Cluster Analysis
Let us understand this through a small example. Consider, city network as a huge graph and now plans to deploy telephone lines in such a way that in minimum lines we can connect to all city nodes. This is where the spanning tree comes into picture.
Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)
In a weighted graph, a minimum spanning tree is a spanning tree that has minimum weight than all other spanning trees of the same graph. In real-world situations, this weight can be measured as distance, congestion, traffic load or any arbitrary value denoted to the edges.
Minimum Spanning-Tree Algorithm
We shall learn about two most important spanning tree algorithms here −
![]() Kruskal’s Algorithm
Kruskal’s Algorithm
![]() Prim’s Algorithm
Prim’s Algorithm
Both are greedy algorithms.

Comments are closed.