It is a Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) technology and is used for exchanging data over smaller distances. This technology was invented by Ericson in 1994. It operates in the unlicensed, industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) band at 2.4 GHz to 2.485 GHz. Maximum devices that can be connected at the same time are 7. Bluetooth ranges upto 10 meters. It provides data rates upto 1 Mbps or 3 Mbps depending upon the version. The spreading technique which it uses is FHSS (Frequency hopping spread spectrum). A bluetooth network is called piconet and a collection of interconnected piconets is called scatternet.
Bluetooth Architecture:
The architecture of bluetooth defines two types of networks:
1. Piconet
2. Scatternet
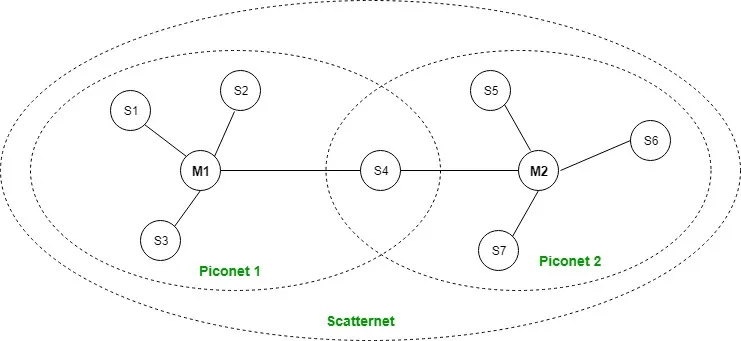
Piconet:
Piconet is a type of bluetooth network that contains one primary node called master node and seven active secondary nodes called slave nodes. Thus, we can say that there are total of 8 active nodes which are present at a distance of 10 metres. The communication between the primary and secondary node can be one-to-one or one-to-many. Possible communication is only between the master and slave; Slave-slave communication is not possible. It also have 255 parked nodes, these are secondary nodes and cannot take participation in communication unless it get converted to the active state.
Scatternet:
It is formed by using various piconets. A slave that is present in one piconet can be act as master or we can say primary in other piconet. This kind of node can receive message from master in one piconet and deliver the message to its slave into the other piconet where it is acting as a slave. This type of node is refer as bridge node. A station cannot be master in two piconets.
Bluetooth protocol stack:
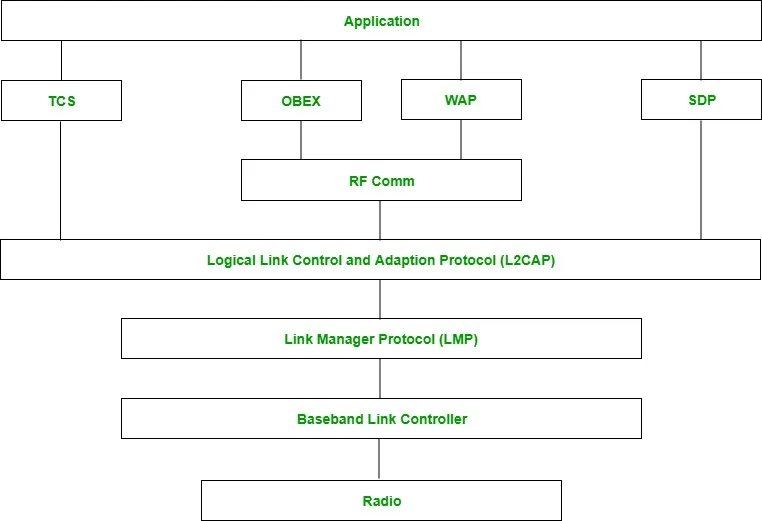
1. Radio (RF) layer:
It performs modulation/demodulation of the data into RF signals. It defines the physical characteristics of bluetooth transceiver. It defines two types of physical link: connection-less and connection-oriented.
2. Baseband Link layer:
It performs the connection establishment within a piconet.
3. Link Manager protocol layer:
It performs the management of the already established links. It also includes authentication and encryption processes.
4. Logical Link Control and Adaption protocol layer:
It is also known as the heart of the bluetooth protocol stack. It allows the communication between upper and lower layers of the bluetooth protocol stack. It packages the data packets received from upper layers into the form expected by lower layers. It also performs the segmentation and multiplexing.
5. SDP layer:
It is short for Service Discovery Protocol. It allows to discover the services available on another bluetooth enabled device.
6. RF comm layer:
It is short for Radio Frontend Component. It provides serial interface with WAP and OBEX.
7. OBEX:
It is short for Object Exchange. It is a communication protocol to exchange objects between 2 devices.
8. WAP:
It is short for Wireless Access Protocol. It is used for internet access.
9. TCS:
It is short for Telephony Control Protocol. It provides telephony service.
10. Application layer:
It enables the user to interact with the application.
Advantages:
· Low cost.
· Easy to use.
· It can also penetrate through walls.
· It creates an adhoc connection immediately without any wires.
· It is used for voice and data transfer.
Disadvantages:
· It can be hacked and hence, less secure.
· It has slow data transfer rate: 3 Mbps.
· It has small range: 10 meters.
Comments are closed.