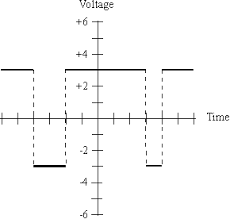
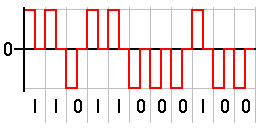
There are two major types of PAMs:
- Single polarity PAM: Here, an appropriate fixed DC bias is integrated with the signal to assure that all pulses are positive.
- Double polarity PAM: Here, the pulses are both negative and positive.
In some PAMs:
- The amplitude of every pulse is directly proportional to instantaneous modulating amplitude when the pulse occurs.
- While in other PAM, the amplitude of every pulse is inversely proportional to instantaneous modulating amplitude when at the occurrence of a pulse.
- In some other systems, the intensity of every pulse is based on particular characteristics of modulating signal other than strength like instantaneous phase or frequency.
Advantages of Pulse Amplitude Modulation
- PAM allows data to be transmitted more effectively, efficiently and quickly using conventional copper wires in greater volume.
- The frequency modulations available are infinite; hence PAM formulas can be developed continually to allow increased data throughput over existing networks.
- PAM is also the simplest form of modulation.