Here the pulses will have the same amplitude. However, one of their timing characteristics is made proportional to the amplitude of the sampled signal. This variable characteristic can be either frequency, position or width. This way pulse time modulation can be classified into three types.
Pulse Width Modulation
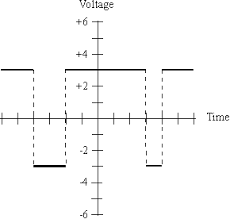
Pulse Width Modulation is also known as pulse duration modulation (PDM). Here, as the name suggests, the width of the pulse is varied in proportional to the amplitude of the signal. Since the width is changing, the power loss can be reduced when compared to PAM signals.

From the figure, it is clear that the amplitude of the signal is constant. Amplitude limiters are used for this. Since clipping of amplitude at desired levels take place, this modulation produces less noise.
Advantages of PTM
- Low power consumption.
- It has an efficiency of about 90 per cent.
- Noise interference is less.
- High power handling capacity.
Disadvantages of PTM
- The circuit is more complex.
- Voltage spikes can be seen.
- The system is expensive as it uses semiconductor devices.
- Switching losses will be more due to high PWM frequency.
Applications of PTM
- Used in encoding purposes in the telecommunication system.
- Used to control brightness in a smart lighting system.
- Helps to prevent overheating in LED’s while maintaining it’s brightness.
- Used in audio and video amplifiers.
Comments are closed.