A line code is the code used for data transmission of a digital signal over a transmission line. This process of coding is chosen so as to avoid overlap and distortion of signal such as inter-symbol interference.
Properties of Line Coding
Following are the properties of line coding −
· As the coding is done to make more bits transmit on a single signal, the bandwidth used is much reduced.
· For a given bandwidth, the power is efficiently used.
· The probability of error is much reduced.
· Error detection is done and the bipolar too has a correction capability.
· Power density is much favorable.
· The timing content is adequate.
· Long strings of 1s and 0s is avoided to maintain transparency.
Types of Line Coding
There are 3 types of Line Coding
- Unipolar
- Polar
- Bi-polar
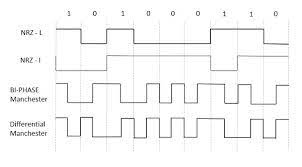
Unipolar Signaling
Unipolar signaling is also called as On-Off Keying or simply OOK.
The presence of pulse represents a 1 and the absence of pulse represents a 0.
There are two variations in Unipolar signaling −
- Non Return to Zero NRZNRZ
- Return to Zero RZRZ
Unipolar Non-Return to Zero NRZNRZ
In this type of unipolar signaling, a High in data is represented by a positive pulse called as Mark, which has a duration T0 equal to the symbol bit duration. A Low in data input has no pulse.
The following figure clearly depicts this.

Advantages
The advantages of Unipolar NRZ are −
- It is simple.
- A lesser bandwidth is required.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of Unipolar NRZ are −
· No error correction done.
· Presence of low frequency components may cause the signal droop.
· No clock is present.
· Loss of synchronization is likely to occur (especially for long strings of 1s and 0s).