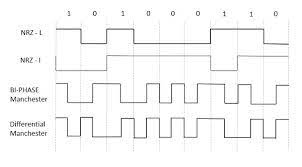
There are two methods of Polar Signaling. They are −
- Polar NRZ
- Polar RZ
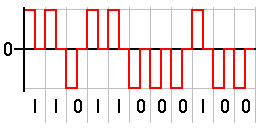
Polar NRZ
In this type of Polar signaling, a High in data is represented by a positive pulse, while a Low in data is represented by a negative pulse. The following figure depicts this well.

Advantages
The advantages of Polar NRZ are −
- It is simple.
- No low-frequency components are present.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of Polar NRZ are −
· No error correction.
· No clock is present.
· The signal droop is caused at the places where the signal is non-zero at 0 Hz.
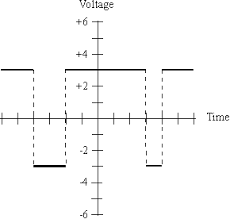
Polar RZ
In this type of Polar signaling, a High in data, though represented by a Mark pulse, its duration T0 is less than the symbol bit duration. Half of the bit duration remains high but it immediately returns to zero and shows the absence of pulse during the remaining half of the bit duration.
However, for a Low input, a negative pulse represents the data, and the zero level remains same for the other half of the bit duration. The following figure depicts this clearly.

Advantages
The advantages of Polar RZ are −
- It is simple.
- No low-frequency components are present.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of Polar RZ are −
· No error correction.
· No clock is present.
· Occupies twice the bandwidth of Polar NRZ.
· The signal droop is caused at places where the signal is non-zero at 0 Hz.