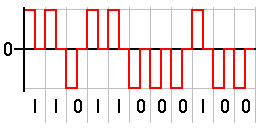
This is an encoding technique which has three voltage levels namely +, – and 0. Such a signal is called as duo-binary signal.
An example of this type is Alternate Mark Inversion AMIAMI. For a 1, the voltage level gets a transition from + to – or from – to +, having alternate 1s to be of equal polarity. A 0 will have a zero voltage level.
Even in this method, we have two types.
- Bipolar NRZ
- Bipolar RZ
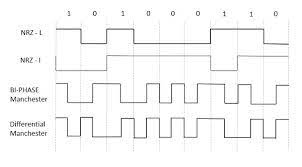
From the models so far discussed, we have learnt the difference between NRZ and RZ. It just goes in the same way here too. The following figure clearly depicts this.

The above figure has both the Bipolar NRZ and RZ waveforms. The pulse duration and symbol bit duration are equal in NRZ type, while the pulse duration is half of the symbol bit duration in RZ type.
Advantages
Following are the advantages −
· It is simple.
· No low-frequency components are present.
· Occupies low bandwidth than unipolar and polar NRZ schemes.
· This technique is suitable for transmission over AC coupled lines, as signal drooping doesn’t occur here.
· A single error detection capability is present in this.
Disadvantages
Following are the disadvantages −
- No clock is present.
- Long strings of data causes loss of synchronization.