MANET is the short form of Mobile AdHoc Network. In ad-hoc networks all the nodes are mobile in nature and hence they can be interfaced dynamically in arbitrary fashion. As we know any wireless transmission has distance coverage limitation, wireless node will utilize its neighbouring nodes to transmit the packet beyond its distance limitation. To overcome this limitation, MANET nodes require ad-hoc type routing protocols. They are of two types viz. table driven routing protocols and On demand routing protocols.
Following are the features of MANET network:
• Dynamic topologies
• variable capacity links
• Energy constrained operation
• Limited physical security
VANET is the short form of Vehicular Adhoc Network. It is subclass of network of MANET type. The routing protocols of MANET are not feasible to be used in the VANET network. If they are used then also they will not be able to deliver required throughput as it has fast changing adhoc network.

In VANET, the communication nodes are moving on pre-defined roads as finalized initially.
The VANET architecture consists of three type of categories as mentioned below:
• cellular and WLAN network
• Pure Ad hoc (network between vehicles and fixed gateways)
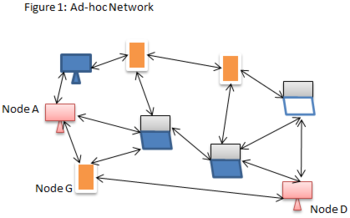
• hybrid(combination of both infrastructure and adhoc networks), as shown in figure.
In the first type, fixed gateways and WiMaX/WiFi APs are used at traffic junctions to connect with the internet, to obtain traffic information and used for routing. The VANET nodes are not subject to storage and power limitation.
MANETs are a kind of wireless ad hoc networks that usually has a routable networking environment on top of a Link Layer ad hoc network. A mobile ad-hoc network (MANET) is a self-configuring infrastructure- less network of mobile devices connected by wireless. Each device in a MANET is free to move independently in any direction, and will therefore change its links to other devices frequently . Vehicular Ad hoc Network (VANET) is a subclass of mobile Ad Hoc networks (MANETs). These networks have no fixed infrastructure and instead rely on the vehicles themselves to provide network functionality.
These networks offer several benefits to organizations of any size. While such a network does pose certain safety concerns but this does not limit VANET‘s potential as a productivity tool. GPS and navigation systems can benefit, as they can be integrated with traffic reports to provide the fastest route to work.



Comments are closed.