APPLICATIONS
· Military battlefield: Ad-Hoc networking would allow the military to take advantage of commonplace network technology to maintain an information network between the soldiers, vehicles, and military information head quarter.
· Collaborative work: For some business environments, the need for collaborative computing might be more important outside office environments than inside and where people do need to have outside meetings to cooperate and exchange information on a given project.
· Local level: Ad-Hoc networks can autonomously link an instant and temporary multimedia network using notebook computers to spread and share information among participants at a e.g. conference or classroom. Another appropriate local level application might be in home networks where devices can communicate directly to exchange information.
· Personal area network and bluetooth: A personal area network is a short range, localized network where nodes are usually associated with a given person. Short-range MANET such as Bluetooth can simplify the inter communication between various mobile devices such as a laptop, and a mobile phone.
· Commercial Sector: Ad hoc can be used in emergency/rescue operations for disaster relief efforts, e.g. in fire, flood, or earthquake. Emergency rescue operations must take place where non-existing or damaged communications infrastructure and rapid
· deployment of a communication network is needed.
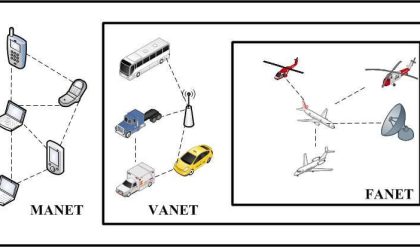
· Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANET) : A mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a continuously self-configuring, infrastructure-less network of mobile devices connected without wires.
· Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs) are used for communication between vehicles and roadside equipment. Intelligent vehicular ad hoc networks (In VANETs) are a kind of artificial intelligence that helps vehicles to behave in intelligent manners during vehicle-to-vehicle collisions, accidents.
· Smart Phone Ad hoc Networks (SPANs) leverage the existing hardware (primarily Bluetooth and Wi-Fi) in commercially available smart phones to create peer-to-peer networks without relying on cellular carrier networks, wireless access points, or traditional network infrastructure.
· Internet based mobile ad hoc networks (iMANETs) are ad hoc networks that link mobile nodes and fixed Internet-gateway nodes. One implementation of this is Persistent System’s Cloud Relay.
· Military / Tactical MANETs are used by military units with emphasis on security, range, and integration with existing systems.